What is the disease?
It’s a common childhood viral infection, mainly affecting young children between 1 and 3 years old. It usually appears in the form of outbreaks, at any time of the year, being more frequent in spring and summer.
How is it spread?
The disease is caused by a family of enteroviruses, the most frequent being Coxsackie A16. It’s easily spread, especially through another sick child’s droplets of saliva; through contact with toys or contaminated objects and through handling faeces. The incubation period varies from 3 to 6 days.
How can you recognise it?
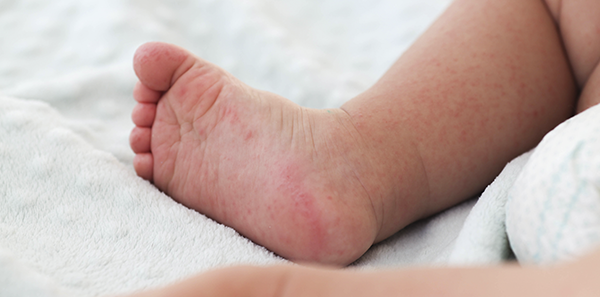
As its name suggests, it usually affects the mouth, with small ulcers both on the tongue and on the palate, lips and peribuccal area; it also affects the hands and feet, with small blisters that can appear both on the palms and on the soles of the feet, and it can often also affect the genital area.
It can be associated with fever and general malaise, with symptoms lasting between 5 and 10 days.
Complications are rare, but one typical side effect is nail loss, especially fingernails, within a few weeks of the infection; this is painless and the nails will grow back.
Is it preventable?
Prevention involves frequent washing of contaminated hands and surfaces. There is no vaccine.
Can it be treated?
Treatment targets the symptoms; antibiotics are not indicated because this is a viral infection.
Analgesics and antipyretics, such as paracetamol, are used to treat any fever and general malaise. Specific gels and oral ointments can be used to relieve pain and discomfort in the mouth. It’s very important to keep the child well-hydrated by frequently offering them small amounts of water and their favourite food, but avoiding hot, salty or acidic meals.
Patricia Andreo Lillo
Paediatrician
San Juan University Hospital