Skin and mucosal tissue fungal infections caused by Candida yeast are extremely common processes that affect a large part of the population at some time in their lives. Candida Albicans is the most frequent and accounts for 70–80% of cases. It normally lives in the digestive tract and in the oral, vaginal and perianal mucosal tissues.
The underlying factors that increase susceptibility to fungal infection (mycosis) include:
- Medical treatments with antibiotics, corticosteroids or contraceptives.
- Humidity. Working in a humid or damp environment. Prolonged exposure to excessive humidity or dampness.
- Obesity. Endocrine disorders and dietary deficiencies like diabetes.
- Inmunodeficiency.
- Pregnancy.
MOST COMMON CLINICAL FORMS
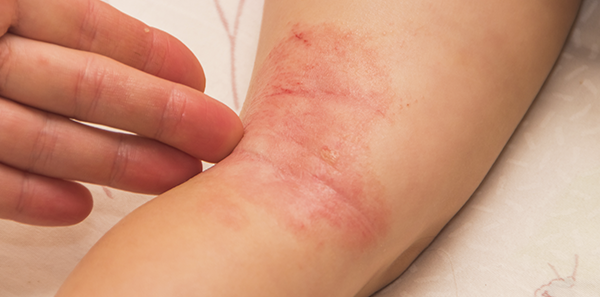
- Candidal Intertrigo. In major skin folds (armpits, groin area, under the breasts, between the buttocks, navel). Especially in women. Usually due to obstruction and humidity.
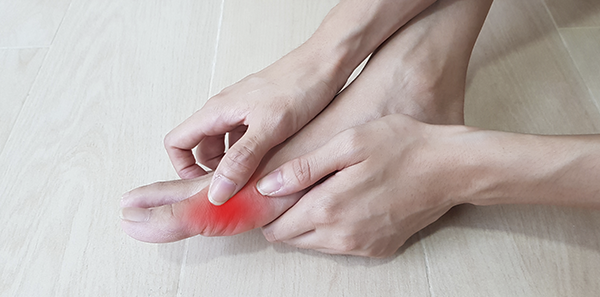
- Candidal Onychomycosis. Nails, hands and feet. More frequent in people who work in damp or humid environments, especially with hands and feet. Waiters, housewives, nurses, sports people (athletes’ foot, etc.).
- Mucosal tissue Candidiasis. Especially oral and vaginal. Muguet, cheilitis, glossitis, thrush, vaginitis and vulvovaginitis.
PREVENTION ADVICE
- If on a long course of antibiotics, use intestinal probiotics and women’s vaginal flora probiotics.
- Avoid being in damp or humid conditions for extended periods of time.
- Wear loose underwear in natural fabrics.
- Ensure correct hygiene. Dry skin folds properly, brush teeth correctly, use mouthwash, etc.
- Maintain correct blood sugar levels.
TREATMENT
Appropriate treatment should concentrate wherever possible on correcting underlying factors. Patients often respond well to local topical therapy, but other times it may be necessary to use some kind of orally administered anti-fungal medication, but the doctor or dermatologist should recommend the best option in each case.