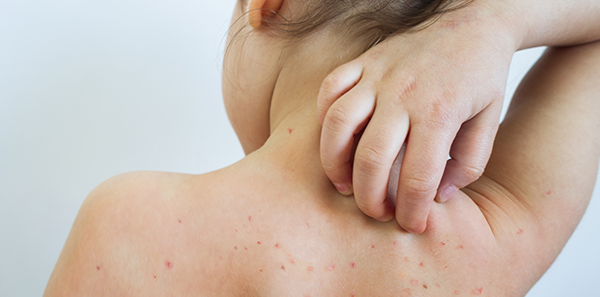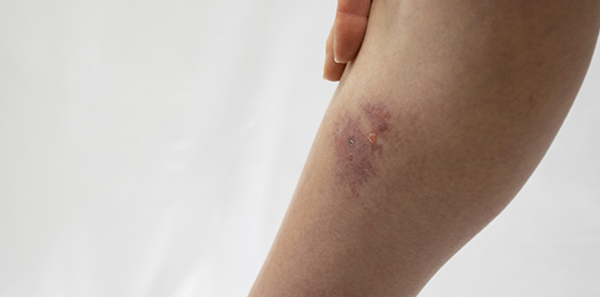
Infectious cellulitis is an acute but not contagious bacterial skin infection, affecting the deeper layers of the dermis, especially the subcutaneous tissue. The most frequent bacteria causing infection tend to be streptococci and staphylococci. Plus, the lower limbs of the body can often be affected.
As a result of infection, the following symptoms can be observed:
- Redness in the area
- Inflammation
- Pain
- Heat in the affected area
Sometimes, the following may also be seen:
- Fever
- Oedema due to accumulation of liquid coming from the blood vessels
- Swelling in the area because the lymphatic vessels are affected
The most important risk factors for suffering from cellulitis are:
- People with an altered or weakened immune system, as they are more likely to contract cellulitis. Those most at risk are the elderly, diabetics (diabetic foot), AIDS, herpes, etc.
- Lymphedema and diseases affecting blood circulation in the lower limbs are the other most frequent underlying factors.
Whenever you see an infection, whether mild or severe, in the skin, it is vitally important to go to your medical centre urgently so a diagnosis can be made in the shortest possible time and the most suitable treatment for each case can be prescribed.
If it is a case of mild cellulitis, this can be treated with oral antibiotics. But we must be vigilant, since if after 48 hours the patient does not respond well, hospital admission and parenteral treatment will be necessary (intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, etc.) to reduce the risk of sepsis as the body’s extreme response to infection.