Nuclear Medicine is the medical speciality that uses radioactive isotopes, nuclear radiation, electromagnetic variations in the components of the nucleus and similar biophysical techniques for medical prevention, diagnosis, treatment and investigation.
Nuclear Medicine is a branch of medical imaging that supports the majority of medical and surgical specialities in diagnosing and treating a variety of diseases.
Its main disciplines are diagnostic imaging and the treatment of certain diseases by means of radiopharmaceutical drugs.
These are non-invasive techniques, as they only need to be administered to the patient beforehand, usually intravenously. The drug given is a radiopharmaceutical and the choice of which kind to use depends on the tissue, organ or system being examined. A radiopharmaceutical drug consists of a radioactive isotope and a drug vehicle. It emits radioactivity, which is received by the various items of technology equipment involved, such as gamma cameras, SPECT-TC, PET-TC (Positron Emission Tomography) and gamma detector probes.
The types of radiation used are alpha, beta, gamma (electromagnetic) and the radiation produced by positron interaction. This last type and gamma radiation are the ones most often used for diagnosis. Alpha and beta are used for treatment.
In conventional diagnosis, the radionuclide most frequently used in Nuclear Medicine is the technetium-99m metastable isotope (99mTc), which disintegrates with the emission of gamma radiation with an energy of 140 keV.
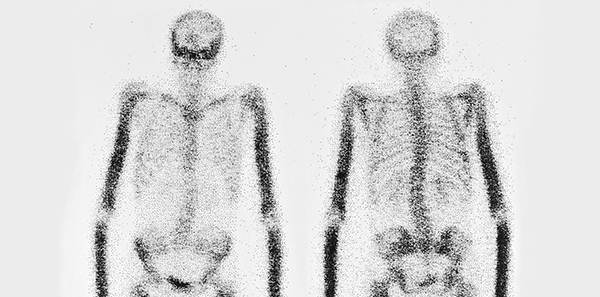
Gamma radiation produces the formation of photons that are detected by the gamma camera and represent the spread of the radiopharmaceutical inside the patient’s body. The computing system allows this to be viewed as an image, known as a GAMMAGRAPH.
An emission image is obtained giving functional information. Nowadays, modern equipment obtains dual, functional and morphological information as most of the equipment is hybrid (gamma camera plus TC or RM).
Positron Emission Tomography is a non-invasive “in vivo” hybrid diagnostic and investigative imaging technique that combines a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) system and a Computerised Axial Tomography (CAT) system in one single piece of equipment. It enables a biochemical and metabolic diagnosis to be obtained with added structural information. The most frequently used positron emitting isotope in clinical practice is Fludeoxyglucose labelled with 18F (18F-FDG).
Currently there are around 100 types of exploratory procedures in Nuclear Medicine that enable the early diagnosis of bone pathology, cardiology, oncology, endocrinology, neurology, nephrology and urology, pulmonology, haematology, digestive system, infectious pathology, peripheral vascular system and paediatrics.
Indications of Nuclear Medicine for diagnosis:
- Endocrinology: thyroid pathology (thyroid cancer, hyperparathyroidism, goitre), parathyroidism, adrenal gland disease and neuroendocrine conditions.
- Gastroenterology: saliva glands, gastric and oesophageal emptying, ectopic gastric mucous, lower limbs, liver disease, digestive and hepatobiliary haemorrhaging.
- Osteoarticulatory.
- In-ammation-infection.
- Neurology: dementia, Parkinson’s disease, Cerebrospinal Fluid Circulation and brain death.
- Pulmonology: perfusion gammagraphy and pulmonary ventilation.
- Nephrology: kidney function pathology, pyelonephritis, kidney transplant, bladder re-ux.
- Cardiology: myocardial perfusion, ventricular function, cardiac short circuits, myocardial damage, myocardial viability and cardiac adrenergic innervation.
- Haematology: erythrocyte volume, erythrokinetics, plaque kinetics and accessory spleen.
- Oncology: main diagnosis, stratication, assessment of control and response to treatment, tumour recurrence, radiotherapy planning, sentinel node and radioguided surgery (ROLL and SNOLL).
Indications of Nuclear Medicine in metabolic therapy:
Treatment of thyroid cancer, hyperthyroidism, hepatic metastases, neuroendocrine tumours, metastatic bone pain, prostate cancer, radioimmunotherapy in lymphomas and radioisotopic synoviorthesis.
Dra. María del Prado Orduña Díez – Doctor of Medicine, Surgeon and Specialist in Nuclear Medicine Clinical Diagnostic Centre
The information published in this media neither substitutes nor complements in any way the direct supervision of a doctor, his diagnosis or the treatment that he may prescribe. It should also not be used for self-diagnosis.
The exclusive responsibility for the use of this service lies with the reader.
ASSSA advises you to always consult your doctor about any issue concerning your health.